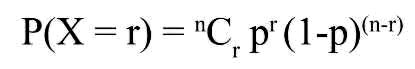Binomial distribution calculator finds the individual & cumulative binomial probabilities of a fixed number of events (n) for a certain number of successes (r) and constant success probability (p). This binomial calculator computes the probability of any event or number of successes “x“ such as: exactly, less than, at most, more than, at least” by using the binomial distribution formula.
Our binomial probability calculator provides all probabilities with detailed steps and graphical representation to visualize the distribution of probabilities.
What is a Binomial Distribution?
Binomial distribution is a statistical distribution that finds the likelihood or probability of a specific number of successes (E) in a fixed number of independent trials (n). Each trial has only two possible outcomes “success or failure” and is known as the Bernoulli trials.
Binomial distribution is the result of a sequence of Bernoulli trials. This distribution is used for discrete events when trials are finite and the probability of success (p) remains constant across all trials. However, if the number of trials is large as (n → ∞) and the probability of success (p) is small, then use the Poisson distribution for approximation.
Binomial Distribution Formula
The probability can be determined for any binomial experiment by using the binomial distribution formula. The formula is mathematically written as:
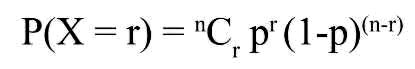
Breakdown of the binomial distribution formula:
- n = Number of trials / events.
- P = Probability of Success
- r = Number of Successes
- 1-p = The failure probability
- nCr = It is the combination of terms and is equal to n! / (r! * (n-r)!)
This formula can be helpful to calculate binomial probabilities manually. But for a large number of “n” and “r” you can use our binomial distribution calculator.
How to Find Probability by Binomial Distribution?
To quickly find the probability of any event then use our above binomial probability distribution calculator. But if you want to do it manually then follow the steps mentioned below and understand how to calculate the binomial distribution.
Example 1:
Find the probability of an “exact head” when a fair coin is flipped 5 times (n=5) and the success of the head is 3 (r=3).
Solution:
Step 1: Now, begin with the collection of data.
Given Data: n = 5, p = 0.5= 1/2, r = 3
Step 2: Put the values in the binomial formula.
P(r) = nCr · pr (1 − p) n−r
P (3) = 5C3 · (1/2)3 (1/2)5-3
Now, simplify:
P (X = 3) = 5C3 (0.5)3 (0.5)2
= (15.5) (0.125) (0.25)
= 0.3125
So, the probability of exactly “3 heads” is P (X = 3) = 0.3125. To verify whether your calculation is correct or not then use our binomial probability calculator.
Frequent Asked Question:
When to use binomial distribution?
The binomial distribution can be used if a set number of experiments or trials(n) are fixed and each trial has only two outcomes (i.e., success or failure & yes or no). Probability of success (p) must be constant and the outcome of each trial is independent of other trials.
For what purposes can binomial distributions be used?
A binomial distribution is used to calculate the probability of a specific number of successes in a fixed number of independent trials. It is used for the prediction or occurrence of any event in different scenarios like quality control checks, surveys with yes/no answers, or coin flips.
What is a negative binomial distribution?
A negative binomial distribution is a probability distribution that represents the number of failures before achieving a fixed number of successes in a series of independent bernoulli trials.
What types of probabilities does this calculator calculate?
Our binomial distribution calculator finds these types of probabilities: P(X=x)=Exactly x, P(X<x)= Less than x, P(X≤x) = At most x, P(X>x) = More than x, and P(X≥x) = At least x.